Nutritional Profile of Cannellini Beans

Cannellini beans nutrition facts – Cannellini beans, also known as white kidney beans, are a nutritional powerhouse, offering a substantial amount of essential nutrients in a relatively low-calorie package. They are a versatile ingredient, easily incorporated into various dishes, making them a convenient way to boost your daily intake of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. This section provides a detailed breakdown of the nutritional composition of cannellini beans.
Macronutrient Composition of Cannellini Beans
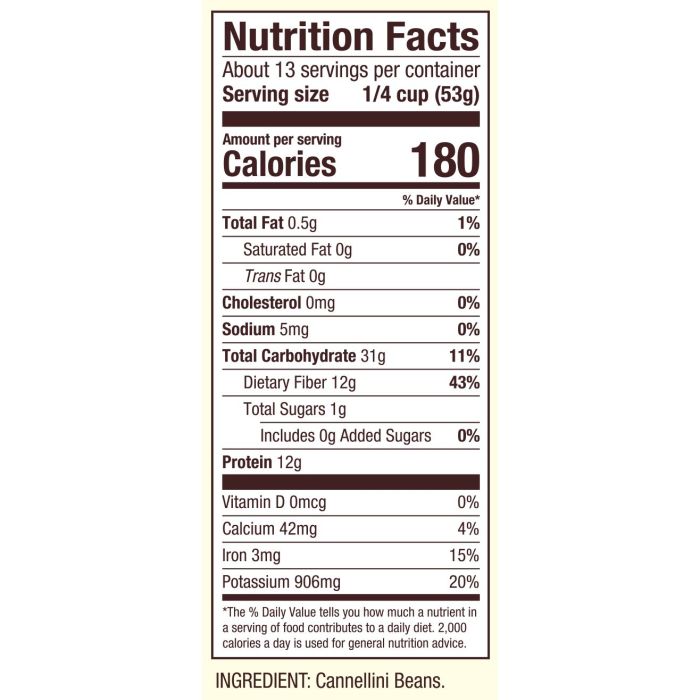
A 100g serving of cooked cannellini beans provides a significant amount of macronutrients crucial for energy and bodily functions. The exact values may vary slightly depending on factors such as growing conditions and cooking methods, but a representative analysis is provided below. These values are approximate and should be considered as general guidelines.
Approximately, a 100g serving contains:
- Protein: ~ 8g (approximately 16% of the recommended daily intake for an average adult, based on a 50g protein daily recommendation).
- Carbohydrates: ~ 18g (this includes both digestible carbohydrates providing energy and dietary fiber contributing to digestive health). The percentage of daily value varies greatly depending on individual caloric needs.
- Fat: ~ 1g (predominantly unsaturated fats, beneficial for heart health).
Vitamins and Minerals in Cannellini Beans
Cannellini beans are an excellent source of several essential vitamins and minerals. The following table summarizes the content per 100g serving:
| Nutrient | Amount (per 100g) | Unit | % Daily Value (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iron | 2.0 | mg | ~11% |
| Folate | 120 | µg | ~30% |
| Potassium | 400 | mg | ~9% |
| Magnesium | 70 | mg | ~18% |
| Zinc | 1.0 | mg | ~9% |
| Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) | 0.3 | mg | ~18% |
| Manganese | 0.8 | mg | ~40% |
Note: Daily value percentages are approximate and can vary depending on individual dietary needs and recommendations.
Fiber Content and Health Benefits
Cannellini beans are particularly rich in dietary fiber, a crucial component for digestive health and overall well-being. A 100g serving contains approximately 7-8g of fiber, a substantial contribution to the recommended daily intake. This fiber is composed of both soluble and insoluble types:
Soluble fiber, such as pectin, helps regulate blood sugar levels and cholesterol. Insoluble fiber promotes regular bowel movements and prevents constipation. The combined effects of these fiber types contribute to improved gut health, reduced risk of heart disease, and better blood sugar control.
Cannellini Beans and Glycemic Index
Cannellini beans, like other legumes, have a relatively low glycemic index (GI), making them a suitable food choice for individuals aiming to manage their blood sugar levels. Understanding the GI of cannellini beans and how it compares to other foods is crucial for making informed dietary choices. The glycemic index is a ranking system for carbohydrate-containing foods based on how quickly they raise blood glucose levels after consumption.The glycemic index of cannellini beans is generally considered to be low, typically ranging from 20 to 30.
This low GI value indicates that cannellini beans cause a slow and gradual rise in blood sugar, preventing the sharp spikes associated with high-GI foods. This slow release of glucose is beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those aiming to maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day, promoting sustained energy and reducing the risk of insulin resistance. The fiber content in cannellini beans significantly contributes to their low GI.
Fiber slows down digestion and glucose absorption, preventing rapid blood sugar fluctuations.
Cannellini beans offer a nutritional powerhouse, boasting fiber and protein. It’s a stark contrast to the sugar content found in many popular drinks, like Mountain Dew, where you can check the specifics by looking at the nutrition facts for mtn dew online. Understanding these differences highlights the importance of balanced nutrition, emphasizing the benefits of choosing nutrient-rich foods like cannellini beans over sugary alternatives.
Glycemic Index Comparison of Cannellini Beans with Other Legumes
A comparison with other common legumes helps illustrate cannellini beans’ position within the broader context of carbohydrate-rich foods. The GI values can vary depending on factors like preparation method and specific bean variety. However, the following provides a general comparison:
- Cannellini Beans: 20-30
- Kidney Beans: 29-32
- Pinto Beans: 29-35
- Black Beans: 29-35
- Chickpeas: 28-33
- Lentils: 25-35 (values vary significantly depending on the type of lentil)
As this list shows, cannellini beans fall within a similar GI range to many other legumes, all of which generally exhibit low GI values.
Effect of Preparation Method on Cannellini Bean Glycemic Index, Cannellini beans nutrition facts
The preparation method of cannellini beans can subtly influence their GI. While the differences might not be dramatic, they are worth noting.Dried cannellini beans generally have a slightly lower GI than canned beans. This is likely due to the longer cooking time required for dried beans, which leads to further breakdown of complex carbohydrates and a slower release of glucose into the bloodstream.
Canned beans, having undergone processing, may exhibit a slightly faster glucose absorption rate, resulting in a marginally higher GI. However, the difference is usually minor, and both canned and dried cannellini beans remain low-GI foods. For example, a study might show a difference of only 2-3 GI points between similarly prepared canned and dried cannellini beans. This difference is usually not clinically significant for most individuals.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations: Cannellini Beans Nutrition Facts
While cannellini beans offer a wealth of nutritional benefits, it’s crucial to be aware of potential drawbacks and considerations before incorporating them extensively into your diet. These primarily revolve around antinutrient content and potential interactions with certain health conditions and medications. Understanding these aspects allows for informed and safe consumption.
Cannellini beans, like other legumes, contain antinutrients such as phytic acid and lectins. Phytic acid can bind to minerals like iron and zinc, reducing their absorption. Lectins, on the other hand, can interfere with digestion and potentially cause gastrointestinal discomfort. However, these antinutrient levels can be significantly reduced through proper food preparation methods.
Antinutrient Mitigation
Soaking and cooking are effective strategies to minimize the antinutrient content in cannellini beans. Soaking the beans for at least 8-12 hours before cooking helps break down some of the antinutrients. Thorough cooking, ideally boiling until tender, further reduces their levels. The combination of soaking and cooking is particularly effective in minimizing the potential negative impacts of phytic acid and lectins.
For example, a study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry demonstrated a significant reduction in phytic acid content after soaking and boiling soybeans, a legume closely related to cannellini beans. While specific data for cannellini beans might vary slightly, the principle remains the same.
Medication and Health Condition Interactions
Cannellini beans, due to their high fiber and carbohydrate content, may interact with certain medications. For instance, individuals taking medications for diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels carefully after consuming cannellini beans, as they can impact glucose absorption. Similarly, individuals with digestive issues such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) might experience increased gas or bloating due to the high fiber content.
It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian if you have any concerns about potential interactions with your specific medications or health conditions.
Dietary Recommendations for Specific Needs
Individuals with kidney disease should exercise caution when consuming cannellini beans, as they are relatively high in potassium and phosphorus. These minerals can be problematic for those with impaired kidney function. Limiting cannellini bean intake or consulting a nephrologist or registered dietitian specializing in renal diets is recommended for individuals with kidney disease. Similarly, people on low-FODMAP diets (often prescribed for IBS) may need to limit their consumption, as cannellini beans contain FODMAPs which can exacerbate symptoms for some.
Careful monitoring of individual tolerance is key.
Popular Questions
Are canned cannellini beans as nutritious as dried?
While both offer nutritional benefits, dried cannellini beans generally retain more nutrients after proper preparation. Canned beans may contain added sodium.
Can I eat cannellini beans every day?
Moderation is key. Daily consumption is generally fine for most, but those with kidney issues should consult a doctor.
Do cannellini beans cause gas?
Like other legumes, they can cause gas in some individuals. Soaking and cooking them thoroughly can help reduce this effect.
Are cannellini beans good for weight loss?
Yes, their high fiber and protein content promote satiety, helping with weight management.
Can I freeze cannellini beans?
Yes, both cooked and uncooked cannellini beans can be frozen for later use. Cooked beans should be allowed to cool completely before freezing.








